

EXPLORE.PERSIST.MASTER.
CompTIA Security+ Training Program.
Share :
+971 43346660
Get enrolled for CompTIA Security+ certification training in Dubai from IP Rulers. The CompTIA Security+ certification is a vendor-neutral credential. The CompTIA Security+ exam is an internationally recognized validation of foundation-level security skills and knowledge, and is used by organizations and security professionals around the globe.
The CompTIA Security+ is a globally recognized certification, validating an individual’s fundamental security knowledge and skills. The first goal of the course is to make you a good IT security tech and, in the process, make sure you are ready to pass the CompTIA Security+ exam.
The CompTIA Security+ exam will certify the successful candidate has the knowledge and skills required to install and configure systems to secure applications, networks, and devices; perform threat analysis and respond with appropriate mitigation techniques; participate in risk mitigation activities; and operate with an awareness of applicable policies, laws, and regulations. The successful candidate will perform these tasks to support the principles of confidentiality, integrity, and availability.
CompTIA Security+ is accredited by ANSI to show compliance with the ISO 17024 Standard and, as such, the exam objectives undergo regular reviews and updates. CompTIA exams result from subject matter expert workshops and industry-wide survey results regarding the skills and knowledge required of an IT professional
Required exam: CompTIA Security+ SY0-501
Target Audience:
This course is designed for anyone seeking Cyber Security certification. Specifically, it is recommended that you have the following skills and knowledge before starting this course:
- Know the function and basic features of the components of a PC.
- Use Windows Server to create and manage files and use basic administrative features (Explorer, Control Panel, Server Manager, and Management Consoles).
- Operate the Linux OS using basic command-line tools.
- Know basic network terminology and functions (such as OSI Model, Topology, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, switches, routers).
- Understand TCP/IP addressing, core protocols, and troubleshooting tools
Prerequisite:
The CompTIA Security+ certification is aimed at an IT security professional who Specifically, it is recommended that you have the following skills and knowledge before starting this course:
- Know the function and basic features of the components of a PC.
- Use Windows Server to create and manage files and use basic administrative features (Explorer, Control Panel, Server Manager, and Management Consoles).
- Operate the Linux OS using basic command-line tools.
- Know basic network terminology and functions (such as OSI Model, Topology, Ethernet, Wi-Fi, switches, routers).
- Understand TCP/IP addressing, core protocols, and troubleshooting tools
This course will teach you the fundamental principles of installing and configuring cybersecurity controls and participating in incident response and risk mitigation.
Study of the course can also help to build the prerequisites to study more advanced IT security qualifications, including CompTIA Cybersecurity Analyst (CSA)+, CompTIA Advanced Security Practitioner (CASP), and ISC’s CISSP (Certified Information Systems Security Professional).
On course completion, you will be able to:
- Identify network attack strategies and defenses.
- Understand the principles of organizational security and the elements of effective security policies.
- Know the technologies and uses of cryptographic standards and products.
- Identify network- and host-based security technologies and practices.
- Describe how wireless and remote access security is enforced.
- Describe the standards and products used to enforce security on web and communications technologies.
- Identify strategies for ensuring business continuity, fault tolerance, and disaster recovery.
- Summarize application and coding vulnerabilities and identify development and deployment methods designed to mitigate them.
Duration
40 Hours
Skill Level
Beginner
Certificate
Yes
Modules
6
Language
English
Mode
Online/Offline
Key Highlights
- Live Instructor-Led Training (Online & Classroom)
- 40 Hours of Technology Lectures
- Weekdays (Tue - Fri)
- Friday to Saturday or Saturday to Sunday - Weekend
- Real World Live Scenarios and Migrations
- Exam question bank and Preparation
Key Highlights
- 100% Pass Guarantee
- 24/7 Access to the Learning Resources
- Hands-on Lab Practice on physical equipment
- Flexible Installment Plans
- Boot Camp Training for a Fast Track Learning
- Eve-ng Set up on the laptop with images
- Demand-driven recorded video lectures for references
Course Curriculam
1.1 Given a scenario, analyze indicators of compromise and determine the type of malware.
- Viruses
- Crypto malware
- Ransomware
- Worm
- Trojan
- Rootkit
- Keylogger
- Adware
- Spyware
- Bots
- RAT
- Logic bomb
- Backdoor
1.2 Compare and contrast types of attacks
- Social engineering
- Application/service attacks
- Wireless attacks
- Cryptographic attacks
1.3 Explain threat actor types and attributes.
- Types of actors
- Attributes of actors
- Use of open-source intelligence
1.4 Explain penetration testing concepts.
- Active reconnaissance
- Passive reconnaissance
- Pivot
- Initial exploitation
- Persistence
- Escalation of privilege
- Black box
- White box
- Gray box
- Penetration testing vs. vulnerability scanning
- Explain vulnerability scanning concepts.
- Passively test security controls
- Identify vulnerability
- Identify lack of security controls
- Identify common misconfigurations
- Intrusive vs. non-intrusive
- Credentialed vs. non-credentialed
- False positive
- Explain the impact associated with types of vulnerabilities.
- Race conditions
- Vulnerabilities due to:
- Improper input handling
- Improper error handling
- Misconfiguration/weak configuration
- Default configuration
- Resource exhaustion
- Untrained users
- Improperly configured accounts
- Vulnerable business processes
- Weak cipher suites and implementations
- Memory/buffer vulnerability
- System sprawl/undocumented assets
- Architecture/design weaknesses
- New threats/zero day
- Improper certificate and key management
2.1 Install and configure network components, both hardware and software-based, to support organizational security.
- Firewall
- VPN concentrator
- NIPS/NIDS
- Router
- Switch
- Proxy
- Load balancer
- Access point
- SIEM
- DLP
- NAC
- Mail gateway
- Bridge
- SSL/TLS accelerators
- SSL decryptors
- Media gateway
- Hardware security module
2.2 Given a scenario, use appropriate software tools to assess the security posture of an organization
- Protocol analyzer
- Network scanners
- Wireless scanners/cracker
- Password cracker
- Vulnerability scanner
- Configuration compliance scanner
- Exploitation frameworks
- Data sanitization tools
- Steganography tools
- Honeypot
- Backup utilities
- Banner grabbing
- Passive vs. active
- Command line tools
2.3 Given a scenario, troubleshoot common security issues.
- Unencrypted credentials/clear text
- Logs and events anomalies
- Permission issues
- Access violations
- Certificate issues
- Data exfiltration
- Misconfigured devices
- Weak security configurations
- Personnel issues
- Unauthorized software
- Baseline deviation
- License compliance violation (availability/integrity)
- Asset management
- Authentication issues
2.4 Given a scenario, analyze and interpret output from security technologies.
- HIDS/HIPS
- Antivirus
- File integrity check
- Host-based firewall
- Application whitelisting
- Removable media control
- Advanced malware tools
- Patch management tools
- UTM
- DLP
- Data execution prevention
- Web application firewall
2.5 Given a scenario, deploy mobile devices securely.
- Connection methods
- Mobile device management concepts
- Enforcement and monitoring for:
- Deployment models
2.6 Given a scenario, implement secure protocols.
- Protocols
- Use cases
4.1 Compare and contrast identity and access management concepts
- Identification, authentication, authorization and accounting (AAA)
- Multifactor authentication
- Federation
- Single sign-on
- Transitive trust
4.2 Given a scenario, install and configure identity and access services.
- LDAP
- Kerberos
- TACACS+
- CHAP
- PAP
- MSCHAP
- RADIUS
- SAML
- OpenID Connect
- OAUTH
- Shibboleth
- Secure token
- NTLM
4.3 Given a scenario, implement identity and access management controls.
- Access control models
- Physical access control
- Biometric factors
- Tokens
- Certificate-based authentication
- File system security
- Database security
4.4 Given a scenario, differentiate common account management practices.
- Account types
- General Concepts
- Account policy enforcement
5.1 Explain the importance of policies, plans and procedures related to organizational security
- Standard operating procedure
- Agreement types
- Personnel management
- General security policies
5.2 Summarize business impact analysis concepts.
- RTO/RPO
- MTBF
- MTTR
- Mission-essential functions
- Identification of critical systems
- Single point of failure
- Impact
- Privacy impact assessment
- Privacy threshold assessment
5.3 Explain risk management processes and concepts.
- Threat assessment
- Risk assessment
- Change management
5.4 Given a scenario, follow incident response procedures.
- Incident response plan
- Incident response process
5.5 Summarize basic concepts of forensics.
- Order of volatility
- Chain of custody
- Legal hold
- Data acquisition
- Preservation
- Recovery
- Strategic intelligence/ counterintelligence gathering
- Track man-hours
5.6 Explain disaster recovery and continuity of operation concepts.
- Recovery sites
- Order of restoration
- Backup concepts
- Geographic considerations
- Continuity of operation planning
5.7 Compare and contrast various types of controls.
- Deterrent
- Preventive
- Detective
- Corrective
- Compensating
- Technical
- Administrative
- Physical
5.8 Given a scenario, carry out data security and privacy practices.
- Data destruction and media sanitization
- Data sensitivity labeling and handling
- Data roles
- Data retention
- Legal and compliance
6.1 Compare and contrast basic concepts of cryptography.
- Symmetric algorithms
- Modes of operation
- Asymmetric algorithms
- Hashing
- Salt, IV, nonce
- Elliptic curve
- Weak/deprecated algorithms
- Key exchange
- Digital signatures
- Diffusion
- Confusion
- Collision
- Steganography
- Obfuscation
- Stream vs. block
- Key strength
- Session keys
- Ephemeral key
- Secret algorithm
- Data-in-transit
- Data-at-rest
- Data-in-use
- Random/pseudo-random number generation
- Key stretching
- Implementation vs. algorithm selection
- Perfect forward secrecy
- Security through obscurity
- Common use cases
6.2 Explain cryptography algorithms and their basic characteristics.
- Symmetric algorithms
- Cipher modes
- Asymmetric algorithms
- Hashing algorithms
- Key stretching algorithms
- Obfuscation
6.3 Given a scenario, install and configure wireless security settings.
- Cryptographic protocols
- Authentication protocols
- Methods
6.4 Given a scenario, implement public key infrastructure
- Components
- Concepts
- Types of certificates
- Certificate formats
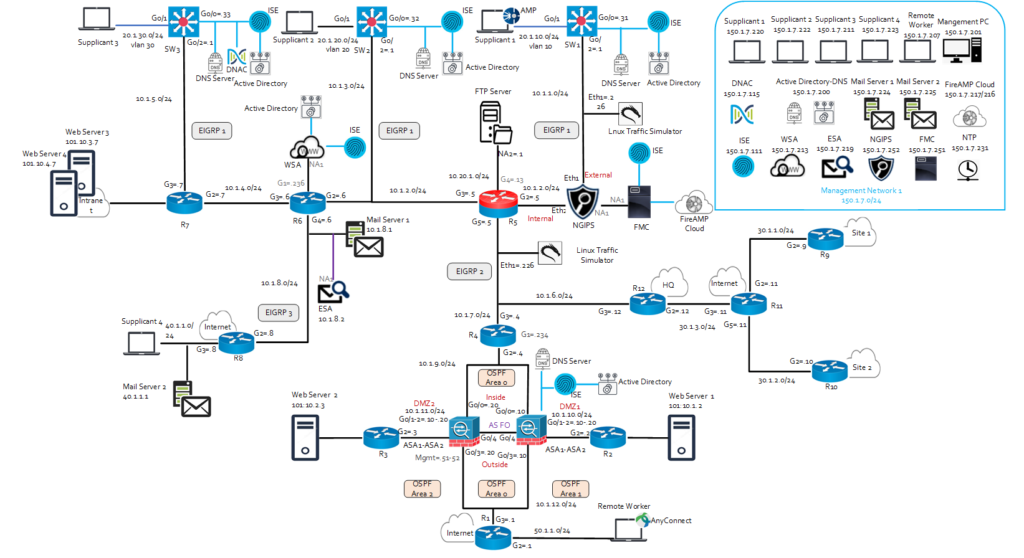
lab infrastructure.

CCIE enterprise infrastructure v1.1 equipment and software list:


The practical exam tests candidates on solutions that can be configured using the below
Equipment and software versions. Candidates may see more recent software versions
during their attempt but will only be tested on features that are supported in the list below.
Passing the exam requires a depth of understanding difficult to obtain without hands-on
experience. Early in your preparation you should arrange access to equipment and soft-
ware similar to that used on the exam.
Virtual machines
- Cisco Catalyst 8000V Routers with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9
- Cisco IOSv with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.8
- Cisco IOSv-L2 with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.2
- Cisco SD-WAN (vManage, vBond, vSmart, cEdge) Software Release 20.9
- Cisco DNA Center, Release 2.3

Physical Equipment
- Cisco Catalyst 9300 Switches with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9 Other (supporting virtual machines)
- Cisco Identity Services Engine 3.1
- Linux Desktop
Topology

Modes Of Training
We provide various modes of training, each catering to different learning styles, preferences, and needs.You can make your choice of training mode.
- Classroom-Based Training
- One-On-One Training
- Online Training
- Corporate Training
- Fast Track Training
- Private Group Training
- Lab Workshop Training
Instructors
MCSE,RHCE,CCNP,CEH,CSA,CCSE,F5-CTS, AWS & Azure
Certified instructor with 20+ years of experience in the field of cloud and cybersecurity. Proven success in leveraging educational theories and methodologies to design, develop, and deliver successful training programs and integrate instructional technology to provide onsite and virtual training. Babu has helped IPRULERS in setting the bar for cloud and cyber security training and helping thousands of engineers to obtain their own certifications. He excels in corporate training and has excellent interpersonal skills that make him stand out. Babu has proven his knowledge and skills in delivering training for the Microsoft, Amazon, f5, Check Point, EC-Council, CompTIA & Cisco etc.

Babu Varghese
Senior Cloud & Security Specialist




