EXPLORE.PERSIST.MASTER.
CCIE Collaboration Certification and Training.
Share :
+971 43346660
CCIE Collaboration Certification v3.0 is the highest and most prestigious certification from Cisco. It ranks No. 1 in the 10 Most Difficult IT Certifications list, and is highly-valued worldwide. A CCIE certified individual is an elite title in the field of network engineering, proving their mastery in their domain of Cisco networking. The CCIE Collaboration Certified experts have the knowledge and skills required to create a clear, mappable, easily handled collaboration solution, in a standard environment.
The CCIE Collaboration program is designed to include Unified Communication UC, conferencing, client services and collaboration endpoints. The quality of the program, the testing methods, and the relevance of this certification enhances its value. At IP Rulers, the classes are facilitated by CCIE Collaboration certified and experienced instructors, and students will be exposed to the latest equipment. With grouped as well as one-to-one classes and online tutorials that could be scheduled for weekdays or weekends in accordance to the students’ choice, IP Rulers is fast becoming a leading name in Dubai,UAE in achieving high-value Cisco Certification with a significant pass rate on the first attempt.
Target Audience:
- Network engineers attempting the core exam – (CLCOR 350- 801)
- Network engineers who have five to seven years of professional experience in designing, deploying, operating and optimizing collaboration technologies.
- Network designers who design and support complex collaboration technologies and topologies.
- Network engineers who use an expert-level problem-solving process (including options analysis) to support complex network technologies and topologies.
- IT students and professionals seeking strong expertise in the subject and an internationally recognized qualification in the same for prospective jobs.
- Candidates with CCNP Collaboration Certification, moving on to expert levels.
- Aspirants in the following job profiles:
- Collaboration Architects
- Unified Communications Architect
- Voice and Video Network Manager
- Network Designer
- Network Administrator
- Consulting Systems Engineer
- Technical Solutions Architect
- Network Manager
- Cisco Integrators and partners
Prerequisites:
- The CCIE Collaboration does not require any particular qualification for attendance of the course. However, comprehensive knowledge of the subjects is necessary for attending the examinations.
- Five to seven years’ experience in the networking field, especially in designing, deploying, operating and optimizing collaboration technologies will be an advantage to attempt the CCIE examination.
- Job roles of elite executives in the fast-paced world of network collaboration.
- Industry-level knowledge and direct experience in implementation of core Cisco collaboration solutions.
- Enhanced job opportunities with sky-high career growth, coupled with respect.
- Expertise in all stages of implementing complex collaboration solutions – from deploying, to operation and optimization.
- Specialist Certification for clearing the qualifying exam
- Authority to link the CCIE Certification Badge to all social media profiles.
Duration
120
Skill Level
Expert
Certificate
Yes
Modules
7
Language
English
Mode
Online/Offline
Key Highlights
- Live Instructor-Led Training (Online & Classroom)
- 120 Hours of Technology Lectures
- 40 Hours of Lab Preparation
- Weekdays (Tue - Fri)
- Weekend (Fri-Sat or Sat-Sun)
- Boot Camp Training for a Fast Track Learning
- Written Question Bank to Clear CLCOR
- Eve-ng Set up on the laptop with images
- A workbook intended for the technology lectures
- Demand-driven recorded video lectures for references
Key Highlights
- Hands-on Lab Practice
- Most Updated and Passable Workbook
- Unlimited Real Rack Access Until you pass or a Version Change
- Support Until you pass or a Version Change
- Detailed Explanation of the Real Lab Solution by the Expert
- Individual Attention given once the real lab preparation started
- 24/7 Access to the Learning Resources
- Flexible Installment Plans
- Instructor support is readily accessible via Email & Whatsapp
Course Curriculam
1.1 IP Collaboration Signaling Protocols
- SIP
- MGCP
1.2 Media Negotiation
- SDP Offer/Answer model
- SDP Early offer, delayed offer, early media
- SDP Payload type interworking
1.3 Media Path Optimization
- Interactive Connectivity Establishment (ICE)
- TURN and STUN
1.4 SIP Headers
- Identity headers (Name, number, URI, Privacy)
- Route headers
- Diversion headers
- CallID, SessionID, and CiscoGUID
1.5 Media Protocols
- RTP/RTCP, SRTP/SRTCP
- Binary Floor Control Protocol (BFCP)
- ActiveControl (iX)
1.6 DTMF Relay
- In-band vs out-of-band
- RFC 2833
- Key Pad Markup Language (KPML)
- Unsolicited NOTIFY
- Interworking
1.7 Messaging Protocols
- XMPP
- SIP/SIMPLE
1.8 Collaboration APIs
- Unified CM Administrative XML (AXL) API
- Webex REST API
- Cisco Meeting Server
- Unified CM User Data Service API
- Java Telephony Application Programming Interface (JTAPI)
2.1 Network Services
- DHCP
- NTP
- DNS
- CDP/LLDP
2.2 Troubleshoot Layer 2 And Layer 3 Network Connectivity Issues
2.3 Quality Of Service For Collaboration Applications And Endpoints On LAN/WAN/WLAN (Cisco IOS-XE And AireOS)
- Identification
- Classification and marking
- Queuing and scheduling
- Congestion management
2.4 Troubleshoot Voice And Video Quality Issues
- Media stream packet loss, jitter, and latency
- Endpoint media quality metrics
- One-way or no-way media
2.5 Call Admission Control
- CUBE
- UCM
- Cisco Expressway Series
2.6 Certificate Management
- CUBE
- UCM and IM&P
- Cisco Expressway Series
- Cisco Meeting Server
3.1 Global dial plans
- Localization and globalization
- Numbering schemes
- Dialing habits
- Interdigit timeouts
- Calling privileges
- Number presentation
3.2 Fundamental dial plan features on Unified CM
- Partitions and calling search spaces
- Translation and transformation patterns
- Urgent priority
- Path selection
3.3 Advanced dial plan features on Unified CM
- Global dial plan replication
- Local route groups
- Emergency Location Groups
3.4 URI and domain-based routing
3.5 Unified CM telephony features
- Call Pickup
- Barge/privacy
- Native call queuing
- Busy Lamp Field (BLF)
3.6 Audio and video codec selection
3.7 SIP trunking
- SIP profiles
- SIP trunk security profiles
- Resiliency
- Mid-call signaling
- Session refresh
3.8 Securing SIP trunks on UCM
3.9 UDS in a multi-cluster environment
- Service discovery
- ILS
- User search
- LDAP proxy
3.10 Unified CM database replication
3.11 Dial plans on CUBE
- Inbound and outbound dial-peers
- Voice translation rules and profiles
- Dial-peer provisioning policy
- Destination server groups
- Destination dial-peer groups
- E.164 pattern maps
- URI-based dialing
- VRF-aware call routing
3.12 SIP-SRST and E-SRST
3.13 Dial plans on Expressway Series
- Transforms
- Search rules
- Zones
4.1 Hardware and software endpoint registration in a multi-cluster environment
- On-premise (local or proxy TFTP)
- Mobile and Remote Access (Service Discovery)
- Cloud
4.2 Mixed mode and Security By Default (SBD) on Unified CM
- Certificate Trust List (CTL) and Identity Trust List (ITL)
- Token-less
- Trust Verification Service (TVS)
4.3 Securing endpoints
4.4 Collaboration endpoints and infrastructure using IPv6
4.5 Endpoint features
- Directory integration and search
- Product specific configuration
- Multistream
4.6 User authentication and authorization
- Directory synchronization On-premise
- Directory synchronization Cloud
- Single-Sign-On (SSO)
- OAuth
4.7 Self-provisioning
5.1 ISDN PRI gateways
5.2 SIP trunks using CUBE
5.3 SIP normalization and SDP normalization
- Normalization and transparency scripts (Lua)
- Cisco IOS-XE SIP profiles
5.4 Securing SIP trunks on CUBE
- SRTP to RTP interworking
- SRTP pass-through
- SRTP to SRTP interworking
5.5 Stateful box-to-box redundancy on CUBE (Cisco IOS-XE)
5.6 Network and application level security on Cisco IOS-XE
- IP Trust List
- Call spike protection
- Media policing
- Call thresholds
- RTP port ranges
- Telephony denial of service attacks
5.7 Firewall traversal in a Collaboration solution
- Port numbers and transport
- NAT
- Web proxy servers
- Deep Packet Inspection considerations
5.8 Expressway Series traversal communications
- Traversal zones
- SSH tunnels
- Encryption interworking
5.9 Mobile and Remote Access (MRA)
5.10 Network and application level security on Expressway Series
- Toll fraud prevention (CPL)
- Zone authentication
- Automated intrusion protection
- Mutual TLS
5.11 Webex Edge and Webex Hybrid Services
- Extending cloud services using on premise resources
- Cloud service management
5.12 Third-party interoperability and federation
- Voice and video calling
- IM&P
6.1 Media resources
- Transcoding and transrating
- MTP
- Music on hold (unicast and multicast)
6.2 Rendezvous conferencing
- Unified CM Conference Now
- Cisco Meeting Server Spaces
6.3 Ad-hoc conferencing
- Cisco IOS-XE conferencing
- Cisco Meeting Server
6.4 Scheduled meetings
- On-premise
- Cloud
6.5 CallBridge and WebBridge on Cisco Meeting Server
- Internal user access
- External user access
6.6 High availability on Cisco Meeting Server
6.7 Secure conferencing on Cisco Meeting Server
7.1 On premise IM&P servers and clients
7.2 Presence
- Busy Lamp Field (BLF)
- Soft client
7.3 IM&P server integration with external database for Persistent Chat and Group Chat
7.4 Cisco Unity Connection voicemail integration
7.5 Cisco Unity Connection voicemail features
- Call and directory handlers
- Voicemail access from soft clients
- Video greetings and messaging
7.6 Cisco Unity Connection voicemail dial plan
- Partitions and search spaces
- Routing rules
7.7 Mobility features
- Mobile Connect (Single Number Reach)
- Device Mobility
- Mobile Identity
- Extend and Connect
- Extension Mobility
7.8 Extension Mobility Cross Cluster (EMCC)
- Emergency dialing considerations
- Certificate exchange
7.9 Audio and video call recording architectures
- SIP-based Media Recording (SIPREC)
- Network-Based Recording
- Built-in bridge
- CUBE Media Proxy
- Cisco Meeting Server
7.10 Secure call recording
7.11 Cisco Unified Contact Center Express (UCCX)
- Integration
- Scripting
7.12 Contact Center agent desktop (Finesse)
lab infrastructure.

CCIE enterprise infrastructure v1.1 equipment and software list:


The practical exam tests candidates on solutions that can be configured using the below
Equipment and software versions. Candidates may see more recent software versions
during their attempt but will only be tested on features that are supported in the list below.
Passing the exam requires a depth of understanding difficult to obtain without hands-on
experience. Early in your preparation you should arrange access to equipment and soft-
ware similar to that used on the exam.
Virtual machines
- Cisco Catalyst 8000V Routers with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9
- Cisco IOSv with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.8
- Cisco IOSv-L2 with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.2
- Cisco SD-WAN (vManage, vBond, vSmart, cEdge) Software Release 20.9
- Cisco DNA Center, Release 2.3

Physical Equipment
- Cisco Catalyst 9300 Switches with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9 Other (supporting virtual machines)
- Cisco Identity Services Engine 3.1
- Linux Desktop
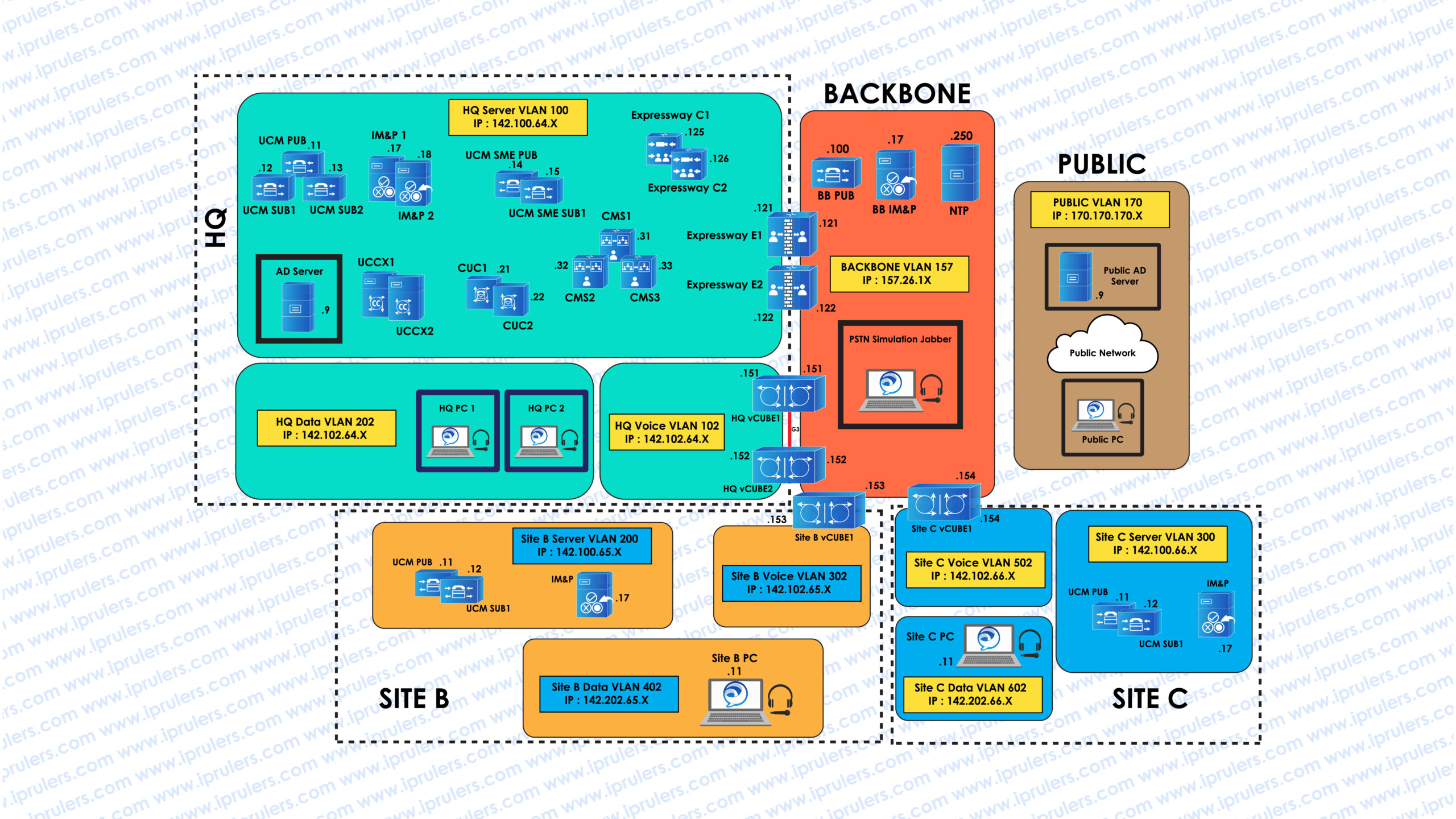
Topology

Modes Of Training
We provide various modes of training, each catering to different learning styles, preferences, and needs.You can make your choice of training mode.
- Classroom-Based Training
- One-On-One Training
- Online Training
- Corporate Training
- Fast Track Training
- Private Group Training
- Lab Workshop Training
Instructors

MD & Founder
4XCCIE (R&S, Security, Collaboration, DC), PCNSE & NSE7
Gigi Vikraman a quadruple CCIE has over 15 years of experience working in the Cisco networking field consulting and training. In addition, he has designed, implemented and supported numerous enterprise networks. He has been a dedicated CCIE instructor for over 10 years. He has extended his service in producing 400+ CCIE’s all over the world. Apart from all these, he has already proven his well knowledge in giving training on Fortinet, Palo Alto and Check Point.
CCIE (R&S, Collaboration), Avaya Python, DevNet
Arvaind, a CCIE Certified professional has been working for different IT companies over the last 8 years. Currently, he works for IPRULERS delivering training and consulting their students in obtaining CCNP & CCIE Certifications.

Aravind C P
Senior Technical Instructor