

EXPLORE.PERSIST.MASTER.
CCNP Service Provider Training & Certification.
Share :
+971 43346660
IP Rulers is the new face of CCNP Service Provider Certification and Training in Dubai, UAE, which provides both online and classroom-based training in the latest cutting-edge technologies in the IT infrastructure and networking portfolio. With grouped as well as one-to-one classes and online tutorials that could be scheduled for weekdays or weekends in accordance to the students’ choice, IP Rulers is fast becoming a leading name in Dubai in providing a highly valued Cisco Certificate, with a 100% pass rate on the first attempt. Students can choose between different concentration topics to go with the core topic to customize their certification, and keep in touch with the dynamic technologies in the field, all with the help of IP Rulers.
The IP Rulers CCNP Service Provider Certification Program is a testimony to a candidate’s service provider skills required for constant upgrading of carrier-grade infrastructure. It provides in-depth technology classes in service provider technologies such as automation and programmability, led by an expert team of trainers who have multiple CCIEs with experience in the industry and hands-on training. Clearing two assessments, one in the core subject, and one in the concentration subject, accrues the Certification, hence enabling focus and customization in any one technical area according to the candidate’s selection.
Target Audience:
- Technical Engineers in the service provider field of IP routing implementation.
- Network Engineers, Network Managers, Network Administrators and Systems Engineers.
- Cisco integrators or partners.
- Network specialists who deliver a carrier infrastructure.
- Network engineers in charge of supporting ISP managed services and other customer requirements.
- Network engineers seeking skill enrichment in specific technologies to nourish their passion and career.
- IT students and professionals seeking strong expertise in the subject and an internationally recognized qualification in the same for prospective jobs.
- Aspirants seeking knowledge in service provider automation and programmability.
Prerequisite:
- The CCNP Service Provider does not require any particular qualification for attendance of the course. However, comprehensive knowledge of the subjects is necessary for attending the examinations.
- A CCNA certificate, or equivalent knowledge, is preferred, but not mandatory.
- Experience in networking field will be an advantage to attempt the CCNP examination.
- Specialist Certification in any CCNP exam, whether it be core or concentration.
- Eligibility to attend the CCIE Service Provider) Lab Exam directly by passing the CCNP Core Examination.
- Customized certification to suit particular areas of technical focus.
- Internationally valued certification from Cisco.
- Skills in Configuration, verification, troubleshooting, and optimization of Service Provider IP network infrastructures and core networks.
- Deep knowledge of Service Provider technologies such as core architecture, services, networking, automation, quality of services, security, and network assurance, through hands-on application and practical instruction.
- Indispensable skills in reinforcement of fundamental concepts in MPLS VPN, and its benefits and classifications.
- Hands-on experience in using modern data models to manage Service Provider network infrastructure.
- Constant acquaintance to the dynamic technologies in the IT field.
- Refreshment in regular concepts of Service Provider Technologies along with Automation.
- Authority to link the CCNP Certification Badge to all social media profiles.
Duration
80
Skill Level
Intermediate
Certificate
Yes
Modules
4
Language
English
Mode
Online/Offline
Key Highlights
- Live Instructor-Led Training (Online & Classroom)
- 80 Hours of Technology Lectures
- Weekdays (Tue - Fri)
- Weekend (Fri-Sat or Sat-Sun)
- Highly Equipped SDN Infra
- Real Equipment and Real World Live Scenarios
- Exam question bank and Preparation
- 100% Pass Guarantee
Key Highlights
- 24/7 Access to the Learning Resources
- Hands-on Lab Practice on physical equipment
- Demand-driven recorded video lectures for references
- Flexible Installment Plans
- Boot Camp Training for a Fast Track Learning
- The Only Center in the UAE with CCIE Service Provider Lab Infra
- Eve-ng Set up on the laptop with images
Course Curriculam
Architecture (15%)
1.1 Describe service provider architectures
- Core architectures (Metro Ethernet, MPLS, unified MPLS, SR)
- Transport technologies (Optical, xDSL, DOCSIS, TDM, and xPON)
- Mobility (packet core, RAN xhaul transport for 4G and 5G)
1.2 Describe Cisco network software architecture
- IOS
- IOS XE
- IOS XR
1.3 Describe service provider virtualization
- NFV infrastructure
- VNF workloads
- OpenStack
1.4 Describe QoS architecture
- MPLS QOS models (Pipe, Short Pipe, and Uniform)
- MPLS TE QoS (MAM, RDM, CBTS, PBTS, and DS-TE)
- DiffServ and IntServ QoS models
- Trust boundaries between enterprise and SP environments
- IPv6 flow label
1.5 Configure and verify control plan security
- Control plane protection techniques (LPTS and CoPP)
- BGP-TTL security and protocol authentication
- BGP prefix suppression
- LDP security (authentication and label allocation filtering)
- BGP sec
- BGP flowspec
1.6 Describe management plane security
- Traceback
- AAA and TACACS
- RestAPI security
- DdoS
1.7 Implement data plane security
- uRPF
- ACLs
- RTBH
Network (30%)
2.1 Implement IS-IS (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Route advertisement
- Area addressing
- Multitopology
- Metrics
2.2 Implement OSPF (v2 and v3)
- Neighbor adjacency
- Route advertisement
- Multiarea (addressing and types)
- Metrics
2.3 Describe BGP path selection algorithm
2.4 Implement BGP (v4 and v6 for IBGP and EBGP)
- Neighbors
- Prefix advertisement
- Address family
- Path selection
- Attributes
- Redistribution
2.5 Implement routing policy language and route maps (BGP, OSPF, IS-IS)
2.6 Troubleshoot routing protocols
- Neighbor adjacency (IS-IS, OSPF, BGP)
- Route advertisement (IS-IS, OSPF, BGP)
2.7 Describe IPv6 transition (NAT44, NAT64, 6RD, MAP, and DS Lite)
2.8 Implement high availability
- NSF / graceful restart
- NSR
- BFD
- Link aggregation
MPLS and Segment Routing (20%)
3.1 Implement MPLS
- LDP sync
- LDP session protection
- LDP neighbors
- Unified MPLS
- MPLS OAM
3.2 Describe traffic engineering
- ISIS and OSPF extensions
- RSVP functionality
- FRR
3.3 Describe segment routing
- Segment types
- IGP control plane
- Segment routing traffic engineering
- TI-LFa
- PCE-PCC architectures
Services (20%)
4.1 Describe VPN services
- EVPN
- Inter-AS VPN
- CSC
- mVPN
4.2 Configure L2VPN and Carrier Ethernet
- Ethernet services (E-Line, E-Tree, E-Access, E-LAN)
- IEEE 802.1ad, IEEE 802.1ah, and ITU G.8032
- Ethernet OAM
- VLAN tag manipulation
4.3 Configure L3VPN
- Intra-AS VPN
- Shared services (extranet and Internet)
4.4 Implement multicast services
- PIM (PIM-SM, PIM-SSM, and PIM-BIDIR)
- IGMP v1/v2/v3 and MLD
4.5 Implement QoS services
- Classification and marking
- Congestion avoidance, traffic policing, and shaping
Automation and Assurance (15%)
5.1 Describe the programmable APIs used to include Cisco devices in network automation
5.2 Interpret an external script to configure a Cisco device using a REST API
5.3 Describe the role of Network Services Orchestration (NSO)
5.4 Describe the high-level principles and benefits of a data modeling language, such as YANG
5.5 Compare agent vs. agentless configuration management tools, such as Chef, Puppet, Ansible, and SaltStack
5.6 Describe data analytics and model-driven telemetry in service provider
5.7 Configure dial-in/out telemetry streams using gRPC
5.8 Configure and verify NetFlow/IPFIX
5.9 Configure and verify NETCONF and RESTCONF
5.10 Configure and verify SNMP (v2c/v3)
Unicast Routing (35%)
1.1 Compare OSPF and IS-IS routing protocols
1.2 Troubleshoot OSPF multiarea operations (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Route advertisement
- Summarization
1.3 Troubleshoot IS-IS multilevel operations (IPv4 and IPv6)
- Route advertisement
- Summarization
1.4 Describe the BGP scalability and performance
- BGP confederations
- Route reflectors
1.5 Troubleshoot BGP
- Route advertisement
- Route reflectors
- Confederations
- Multihoming
- TTL security and inter-domain security
- Maximum prefix
- Route dampening
- Dynamic neighbors
- Communities
1.6 Describe IPv6 tunneling mechanisms
- Static IPv6-in-IPv4 tunnels
- Dynamic 6to4 tunnels
- IPv6 provider edge (6PE)
1.7 Implement fast convergence
- Bidirectional forwarding detection
- Nonstop Forwarding
- NSR
- Timers
- BGP pic (edge and core)
- LFA
- BGP additional and backup path
Multicast Routing (15%)
2.1 Compare multicast concepts
- Multicast domains, distribution trees, and IGMP operations
- Any-Source Multicast (ASM) versus Source Specific Multicast (SSM)
- Intra-domain versus inter-domain multicast routing
2.2 Describe multicast concepts
- Mapping of multicast IP addresses to MAC addresses
- Multiprotocol BGP for IPv4 and IPv6
- Principles and operations of PIM-SM
- Multicast Source Discovery Protocol (MSDP) operations
- MLDP/P2MP
2.3 Implement PIM-SM operations
- Auto-RP, PIMv2 BSR, anycast RP
- BIDIR-PIM operations
- SSM operations
- MSDP operations
2.4 Troubleshoot multicast routing
- Single domain
- Multidomain
Routing Policy and Manipulation (25%)
3.1 Compare routing policy language and route maps
3.2 Describe conditional matching
- Operations
- Semantics of policy applications and statements
- Regular expressions
- Policy sets
- Tags
- ACLs
- Prefix lists and prefix sets
- Route types
- BGP attributes and communities
- Hierarchical and parameterized structures
3.3 Troubleshoot route manipulation for IGPs
- IS-IS
- OSPF
3.4 Troubleshoot route manipulation for BGP
- Route filtering
- Traffic steering
MPLS and Segment Routing (25%)
4.1 Troubleshoot MPLS
- LDP
- LSP
- Unified BGP
- BGP free core
- RSVP TE tunnels
4.2 Implement segment routing
- Routing protocol extensions (OSPF, IS-IS, BGP)
- SRGB and SRLB
- Topology-Independent Loop-Free Alternate (TI-LFA)
- Migration procedures (SR prefer and mapping server)
4.3 Describe segment routing traffic engineering
- Automated steering and coloring
- Policies (constraints, metrics, and attributes)
- PCE-based path calculation
4.4 Describe segment routing v6 (SRv6)
- Control plane operations
- Data plane operations
VPN Architecture(25%)
1.1 Compare VPN architecture
- Layer 2 and Layer 3 VPN
- Inter-AS and Intra-AS
1.2 Troubleshoot underlay
- Core IGP
- LSP
1.3 Describe Layer 2 service architecture
- IOS XR Ethernet Flowpoints
- IOS XE Ethernet Virtual Circuits
1.4 Describe the L3VPN control plane operation
- MP-BGP
- Route distinguisher
- VPNv4 address
- Route target
- VPN label
- VRF routing instance
- PE-CE route advertisement
1.5 Describe the L3VPN data plane operation
- Underlay label
- VRF forwarding instance
Layer 2 VPNs (30%)
2.1 Troubleshoot L2VPN Services
- E-LAN
- E-Line
- E-Tree
2.2 Describe EVPN concepts
- Data plane and control plane operation
- Multihoming mechanisms
- Suppression mechanisms
- Traffic forwarding operation
2.3 Implement Ethernet Operations, Administration, and Maintenance (E-OAM)
2.4 Implementing EVPN
- EVPN IRB
- EVPN VPWS
- EVPN native
Layer 3 VPNs (30%)
3.1 Describe routing requirements
- MP-BGP
- PE-CE routing protocol
3.2 Troubleshoot Intra-AS L3VPNs
- PE-CE
- PE-PE
- PE-RR
3.3 Implement multicast VPN
- Intranet MVPN
- Extranet MVPN
- MLDP
3.4 Implement extranet/shared services
- Import and export route targets
- Route policy
3.5 Describe Inter-AS L3VPNs
- Option A
- Option B
- Option AB
- Option C
3.6 Describe CSC concepts
IPv6 VPNs(10%)
4.1 Describe routing requirements
- MP-BGP
- PE-CE routing protocol
4.2 Troubleshoot IPv6 VPN provider edge
- PE-PE
- PE-CE
Network Programmability and Foundation (10%)
1.1 Utilize common version control operations with git (add, clone, push, commit, diff, branching, and merging conflict)
1.2 Describe characteristics of API styles (REST and RPC)
1.3 Describe the challenges encountered and patterns used when consuming APIs synchronously and asynchronously
1.4 Interpret Python scripts containing data types, functions, classes, conditions, and looping
1.5 Describe the benefits of Python virtual environments
1.6 Explain the benefits of using network configuration tools such as Ansible and Puppet for automating IOS XE or IOS XR platforms
Automation API and Protocols (30%)
2.1 Describe the characteristics and use of YANG Data Models (OpenConfig, IETF, and Vendor)
2.2 Describe common HTTP authentication mechanisms (basic, token, and oauth)
2.3 Compare common data types (JSON, XML, YAML, plain text, gRPC, and protobuf)
2.4 Identify the JSON instance based on a YANG model
2.5 Identify the XML instance based on a YANG model
2.6 Interpret a YANG module tree generated by pyang
2.7 Implement configuration and operation management using RESTCONF protocol
2.8 Implement configuration and operation management using NETCONF protocol
2.9 Compare the NETCONF datastores
Network Device Programmability (30%)
3.1 Deploy device configuration and validate operational state using ncclient
3.2 Construct a Python script using NETCONF with YDK
3.3 Deploy device configuration and validate operational state using NetMiko
3.4 Deploy device configuration and validate operational state using Ansible playbooks
3.5 Compare gNMI with NETCONF
3.6 Construct a Python script using RESTCONF with JSON
3.7 Construct Xpath notation for a given node or instance of a node
3.8 Diagnose model-driven dial-in/-out telemetry streams with gRPC for a Cisco IOS XR
Automation and Orchestration Platforms (30%)
4.1 Describe ETSI NFV
4.2 Describe NSO architecture
4.3 Identify the benefits of NSO
4.4 Construct a Python script to configure a device using NSO RESTCONF API
4.5 Describe the management and automation of Cisco ESC components
4.6 Implement XR traffic controller (including topology information transfer to XTC)
4.7 Identify the uses of Cisco WAE
4.8 Construct a service template using NSO
4.9 Deploy a service package using NSO
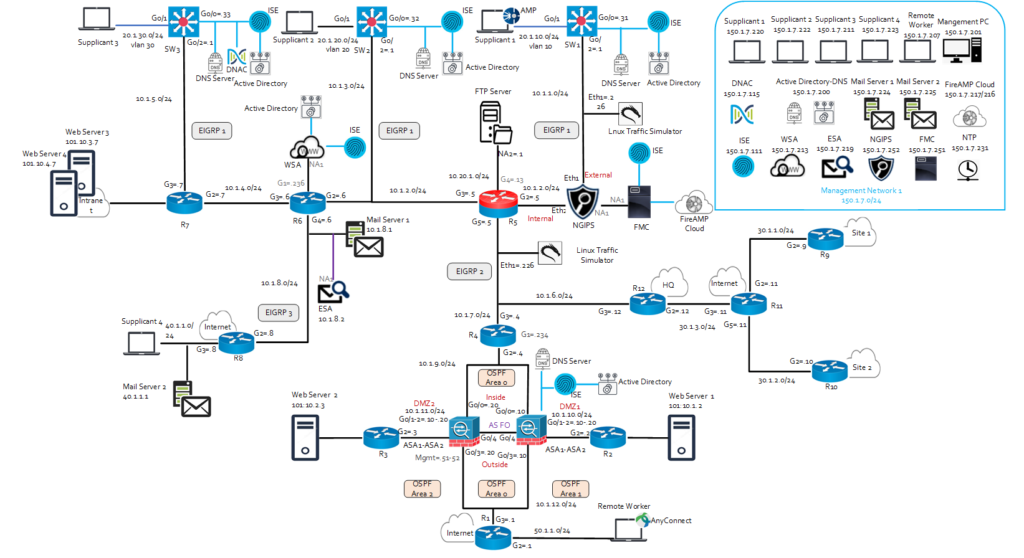
lab infrastructure.

CCIE enterprise infrastructure v1.1 equipment and software list:


The practical exam tests candidates on solutions that can be configured using the below
Equipment and software versions. Candidates may see more recent software versions
during their attempt but will only be tested on features that are supported in the list below.
Passing the exam requires a depth of understanding difficult to obtain without hands-on
experience. Early in your preparation you should arrange access to equipment and soft-
ware similar to that used on the exam.
Virtual machines
- Cisco Catalyst 8000V Routers with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9
- Cisco IOSv with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.8
- Cisco IOSv-L2 with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.2
- Cisco SD-WAN (vManage, vBond, vSmart, cEdge) Software Release 20.9
- Cisco DNA Center, Release 2.3

Physical Equipment
- Cisco Catalyst 9300 Switches with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9 Other (supporting virtual machines)
- Cisco Identity Services Engine 3.1
- Linux Desktop
Topology

Modes Of Training
We provide various modes of training, each catering to different learning styles, preferences, and needs.You can make your choice of training mode.
- Classroom-Based Training
- One-On-One Training
- Online Training
- Corporate Training
- Fast Track Training
- Private Group Training
- Lab Workshop Training
Instructors

gigi vikraman
MD & Founder
4XCCIE (R&S, Security, Collaboration, DC), PCNSE & NSE7
Gigi Vikraman a quadruple CCIE has over 15 years of experience working in the Cisco networking field consulting and training. In addition, he has designed, implemented and supported numerous enterprise networks. He has been a dedicated CCIE instructor for over 10 years. He has extended his service in producing 400+ CCIE’s all over the world. Apart from all these, he has already proven his well knowledge in giving training on Fortinet, Palo Alto and Check Point.




