

EXPLORE.PERSIST.MASTER.
CompTIA Linux+ Training Program.
Share :
+971 43346660
Ip Rulers is one of he best CompTIA+ Training institute in Dubai now and can help you master the course in the shortest time possible. CompTIA Linux+ measures the necessary skills of an IT professional with hands-on experience configuring, monitoring, and supporting servers running the Linux operating system. Successful candidates will have the knowledge required to configure, manage, operate, and troubleshoot a Linux environment by using security best practices, scripting, and automation. These content examples are meant to clarify the test objectives and should not be construed as a comprehensive listing of all the content of this examination
The core objective of our CompTIA Linux+ certification classes is to provide necessary skills that help in easily maintaining the Linux systems. As Linux is flexible, many companies are switching on to use Linux. So, if you have this certification, companies will know that you have the exceptional skill in Linux administration, troubleshooting, and operation. The demand for these experts is mounting year after year and you must soon equip yourself with Linux+ certification otherwise you may not survive if you are in this field.
The CompTIA Linux+ exam is accredited by the American National Standards Institute (ANSI) to show compliance with the International Organization for Standardization (ISO) 17024 Standard and, as such, undergoes regular reviews and updates to the exam objectives.
Required exam: CompTIA Linux+ XK0-004
Target Audience:
This course is designed for anyone seeking CompTIA Linux+ certification. The course also provides foundational knowledge for all support technology involved in the basic installation, operation, and verification of Linux Operating system.
The job roles best suited to the material in this course are:
- System Administrator
- Professionals in the IT and related technologies sector
- Customer Support Engineer
- System Analyst
- IT students and graduates
Prerequisite:
Basic familiarity in any Operating System.
Configure kernel modules, network parameters, and storage, cloud, and virtualization technologies
- System Operation & Maintenance
Manage software and services, and explain server roles, job scheduling, and the use and operation of Linux devices
- Security
Understand best practices for permissions and authentication, firewalls, and file management.
- Linux Troubleshooting & Diagnostics
Analyze system properties and processes and troubleshoot user, application and hardware issues
- Automation & Scripting
Execute basic BASH scripts, version control using Git, and orchestration processes
Duration
40 Hours
Skill Level
Beginner
Certificate
Yes
Modules
5
Language
English
Mode
Online/Offline
Key Highlights
- Live Instructor-Led Training (Online & Classroom)
- 40 Hours of Technology Lectures
- Weekdays (Tue - Fri)
- Friday to Saturday or Saturday to Sunday - Weekend
- Real World Live Scenarios and Migrations
- Exam question bank and Preparation
Key Highlights
- 100% Pass Guarantee
- 24/7 Access to the Learning Resources
- Hands-on Lab Practice on physical equipment
- Flexible Installment Plans
- Boot Camp Training for a Fast Track Learning
- Demand-driven recorded video lectures for references
- Eve-ng Set up on the laptop with images
Course Curriculam
1.1 Explain Linux boot process concepts.
- Boot loaders
- Boot options
- Boot modules and files
- Kernel panic
1.2 Given a scenario, install, configure, and monitor kernel modules.
- Commands
- Locations
1.3 Given a scenario, configure and verify network connection parameters.
- Diagnostic tools
- Configuration files
- Bonding
1.4 Given a scenario, manage storage in a Linux environment.
- Basic partitions
- File system hierarchy
- Device mapper
- Tools
- Location
- File system types
1.5 Compare and contrast cloud and virtualization concepts and technologies
- Templates
- Bootstrapping
- Storage
- Network considerations
- Types of hypervisors
- Tools
Given a scenario, configure localization options.
1.File locations
2.Commands
3.Environment variables
4.Character sets
2.1 Given a scenario, manage users and groups.
- Creation
- Modification
- Deletion
- Queries
- Quotas
- Profiles
- Important files and file contents
2.2 Given a scenario, create, modify, and redirect files
- Text editors
- File readers
- Output redirection
- Text processing
- File and directory operations
2.3 Given a scenario, manage services.
- System management
- SysVinit
2.4 Summarize and explain server roles.
- NTP
- SSH
- Web
- Certificate authority
- Name server
- DHCP
- File servers
- Authentication server
- Proxy
- Logging
- Containers
- VPN
- Monitoring
- Database
- Print server
- Mail server
- Load balancer
- Clustering
2.5 Given a scenario, automate and schedule jobs.
- Cron
- At
- Crontab
- Fg
- Bg
- &
- Kill
- Ctrl+c
- Ctrl+z
- Nohup
2.6 Explain the use and operation of Linux devices.
- Types of devices
- Monitoring and configuration tools
- File locations
- Hot pluggable devices
2.7 Compare and contrast Linux graphical user interfaces.
- Servers
- GUI
- Remote desktop
- Console redirection
- Accessibility
3.1 Given a scenario, apply or acquire the appropriate user and/or group permissions and ownership.
- File and directory permissions
- Context-based permissions
- Privilege escalation
- User types
3.2 Given a scenario, configure and implement appropriate access and authentication methods.
- PAM
- SSH
- TTYs
- PTYs
PKI - VPN as a client
3.3 Summarize security best practices in a Linux environment.
- Boot security
- Additional authentication methods
- Importance of disabling root login via SSH
- Password-less login
- Chroot jail services
- No shared IDs
- Importance of denying hosts
- Separation of OS data from application data
- Change default ports
- Importance of disabling or uninstalling unused and
- unsecure services
- Importance of enabling SSL/TLS
- Importance of enabling auditd
- CVE monitoring
- Discouraging use of USB devices
- Disk encryption
- Restrict cron access
- Disable Ctrl+Alt+Del
- Add banner
3.4 Given a scenario, implement logging services.
- Key file locations
- Log management
- lastb
3.5 Given a scenario, implement and configure Linux firewalls.
- Access control lists
- Technologies
- IP forwarding
- Dynamic rule sets
- Common application firewall configurations
3.6 Given a scenario, backup, restore, and compress files.
- Archive and restore utilities
- Compression
- Backup types
- Off-site/off-system storage
- Integrity checks
4.1 Given a scenario, analyze system properties and remediate accordingly.
- Network monitoring and configuration
- Storage monitoring and configuration
- CPU monitoring and configuration
- Memory monitoring and configuration
- Lost root password
4.2 Given a scenario, analyze system processes in order to optimize performance.
- Process management
4.3 Given a scenario, analyze and troubleshoot user issues
4.4 Given a scenario, analyze and troubleshoot application and hardware issues.
- Permissions
- Access
- Authentication
- File creation
- Insufficient privileges for authorization
- Environment and shell issues
4.5 Given a scenario, analyze and troubleshoot application and hardware issues
- SELinux context violations
- Storage
- Firewall
- Permission
- Dependencies
- Troubleshooting additional hardware issues
5.1 Given a scenario, deploy and execute basic BASH scripts
- Shell environments and shell variables
- #!/bin/bash
- Sourcing scripts
- Directory and file permissions
- Extensions
- Commenting
- File globbin
- Shell expansions
- Redirection and piping
- Exit codes
- Metacharacters
- Positional parameters
- Looping constructs
- Conditional statements
- Escaping characters
5.2 Given a scenario, carry out version control using Git.
- Arguments
- Files
5.3 Summarize orchestration processes and concepts.
- Agent
- Agentless
- Procedures
- Attributes
- Infrastructure automation
- Infrastructure as code
- Inventory
- Automated configuration management
lab infrastructure.

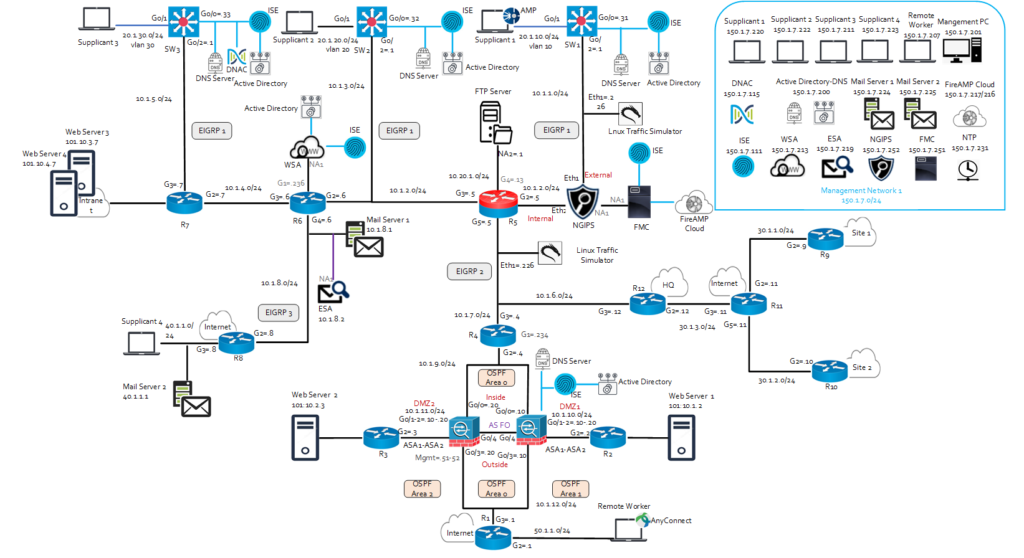
CCIE enterprise infrastructure v1.1 equipment and software list:


The practical exam tests candidates on solutions that can be configured using the below
Equipment and software versions. Candidates may see more recent software versions
during their attempt but will only be tested on features that are supported in the list below.
Passing the exam requires a depth of understanding difficult to obtain without hands-on
experience. Early in your preparation you should arrange access to equipment and soft-
ware similar to that used on the exam.
Virtual machines
- Cisco Catalyst 8000V Routers with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9
- Cisco IOSv with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.8
- Cisco IOSv-L2 with Cisco IOS Software Release 15.2
- Cisco SD-WAN (vManage, vBond, vSmart, cEdge) Software Release 20.9
- Cisco DNA Center, Release 2.3

Physical Equipment
- Cisco Catalyst 9300 Switches with Cisco IOS XE Software Release 17.9 Other (supporting virtual machines)
- Cisco Identity Services Engine 3.1
- Linux Desktop
Topology

Modes Of Training
We provide various modes of training, each catering to different learning styles, preferences, and needs.You can make your choice of training mode.
- Classroom-Based Training
- One-On-One Training
- Online Training
- Corporate Training
- Fast Track Training
- Private Group Training
- Lab Workshop Training
Instructors
MCSE,RHCE,CCNP,CEH,CSA,CCSE,F5-CTS, AWS & Azure
Certified instructor with 20+ years of experience in the field of cloud and cybersecurity. Proven success in leveraging educational theories and methodologies to design, develop, and deliver successful training programs and integrate instructional technology to provide onsite and virtual training. Babu has helped IPRULERS in setting the bar for cloud and cyber security training and helping thousands of engineers to obtain their own certifications. He excels in corporate training and has excellent interpersonal skills that make him stand out. Babu has proven his knowledge and skills in delivering training for the Microsoft, Amazon, f5, Check Point, EC-Council, CompTIA & Cisco etc.

Babu Varghese
Senior Cloud & Security Specialist




