

EXPLORE.PERSIST.MASTER.
Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer (PCNSE).
Share :
+971 43346660
A Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer (PCNSE) is capable of designing, deploying, configuring, maintaining and trouble-shooting the vast majority of Palo Alto Networks Operating Platform implementations.Our team of experts has composed this Palo Alto PCNSE guide to provide the overview about Palo Alto Network Security Engineer exam, and ways to interpret the exam objectives to help you assess your readiness for the Palo Alto PCNSE PAN-OS 11.0 exam by identifying prerequisite areas of knowledge.
IPRulers is the new face of Security Certification and Training in Dubai, UAE, which provides both online and classroom-based training in the latest cutting-edge fundamental technologies in the IT sector. With grouped as well as one-to-one classes and online tutorials that could be scheduled for weekdays or weekends in accordance to the students’ choice, IPRulers is fast becoming a leading name in Dubai in providing a highly valued Cisco Certificate, with a 100% pass rate on the first attempt. Successful completion of this five-day, instructor-led course should enhance the student’s understanding of how to configure and manage Palo Alto Networks next-generation firewalls. The student should learn and get hands-on experience configuring, managing, and monitoring a firewall in a lab environment, all with the help of IPRulers.
Target Audience:
- Network Security Engineer
- Network Engineer
- Network Architect
- Security Consultant, (Computing / Networking / Information Technology)
- Senior Security Consulta
- Security Engineer
- Sr. Network Engineer
Prerequisite:
Students must have completed the Firewall
Essentials: Configuration and Management EDU-210) class.
Recommended Training:
- Mandatory Training: Panorama 11.0 Managing Firewalls
at Scale (EDU-220) - Optional training: Firewall 11.0: Troubleshooting (EDU-330)
The Palo Alto Networks Panorama 9.1: Managing Firewalls at Scale (EDU-220) course is instructor-led training that will help you:
- Learn how to configure and manage the next-generation Panorama™ management server
- Gain experience configuring templates (including template variables) and device groups
- Gain experience with administration, log collection, and logging and reporting
- Become familiar with planning and design considerations for Panorama deployment
Required Exam : PCNSE
Duration
40 Hours
Skill Level
Expert
Certificate
Yes
Modules
6
Language
English
Mode
Online/Offline
Key Highlights
- Live Instructor-Led Training (Online & Classroom)
- 40 Hours of Technology Lectures
- Weekdays (Tue - Fri)
- Friday to Saturday or Saturday to Sunday - Weekend
- Real Equipment and Real World Live Scenarios
- Exam question bank and Preparation
Key Highlights
- 100% Pass Guarantee
- 24/7 Access to the Learning Resources
- Hands-on Lab Practice on physical equipment
- Flexible Installment Plans
- Boot Camp Training for a Fast Track Learning
- Demand-driven recorded video lectures for references
- Training & Practice on Physical & Licensed Equipment
Course Curriculam
Domain Weight(%)
Core Concepts 12%
Deploy and Configure Core Components 20%
Deploy and Configure Features and Subscriptions 17%
Deploy and Configure Firewalls Using Panorama 17%
Manage and Operate 16%
Troubleshooting 18%
1.1 Identify how Palo Alto Networks products work together to improve PAN-OS services
1.1.1 Security components
1.1.2 Firewall components
1.1.3 Panorama components
1.1.4 PAN-OS subscriptions and the features they enable
1.1.5 Plug-in components
1.1.6 Heatmap and BPA reports
1.1.7 Artificial intelligence operations (AIOps)/Telemetry
1.1.8 IPv6
1.1.9 Internet of things (IoT)
1.2 Determine and assess appropriate interface or zone types for various environments
1.2.1 Layer 2 interfaces
1.2.2 Layer 3 interfaces
1.2.3 Virtual wire (vwire) interfaces
1.2.4 Tap interfaces
1.2.5 Subinterfaces
1.2.6 Tunnel interfaces
1.2.7 Aggregate interfaces
1.2.8 Loopback interfaces
1.2.9 Decrypt mirror interfaces
1.2.10 VLAN interfaces
1.3 Identify decryption deployment strategies
1.3.1 Risks and implications of enabling decryption
1.3.2 Use cases
1.3.3 Decryption types
1.3.4 Decryption profiles and certificates
1.3.5 Create decryption policy in the firewall
1.3.6 Configure SSH Proxy
1.4 Enforce User-ID
1.4.1 Methods of building user-to-IP mappings
1.4.2 Determine if User-ID agent or agentless should be used
1.4.3 Compare and contrast User-ID agents
1.4.4 Methods of User-ID redistribution
1.4.5 Methods of group mapping
1.4.6 Server profile & authentication profile
1.5 Determine how and when to use the Authentication policy
1.5.1 Purpose of, and use case for, the Authentication policy
1.5.2 Dependencies
1.5.3 Captive portal versus GlobalProtect (GP) client
1.6 Differentiate between thefundamental functions that reside on the management plane and data plane
1.7 Define multiple virtual systems (multi-vsys) environment
1.7.1 User-ID hub
1.7.2 Inter-vsys routing
1.7.3 Service routes
1.7.4 Administration
2.1 Configure management profiles
2.1.1 Interface management profile
2.1.2 SSL/TLS service profile
2.2 Deploy and configure Security profiles
2.2.1 Custom configuration of different Security profiles and Security profile groups
2.2.2 Relationship between URL filtering and credential theft prevention
2.2.3 Use of username and domain name in HTTP header insertion.
2.2.4 DNS Security2.2.5 How to tune or add exceptions to a Security profile
2.2.6 Compare and contrast threat prevention and advanced threat prevention
2.2.7 Compare and contrast URL Filtering and Advanced URL Filtering
Task 2.3 Configure zone protection, packet buffer protection, and DoS
protection
2.3.1 Customized values versus default settings
2.3.2 Classified versus aggregate profile types
2.3.3 Layer 3 and Layer 4 header inspection
2.4 Design the deployment configuration of a Palo Alto Networks firewall
2.4.1 Advanced high availability (HA) deployments
2.4.2 HA pair
2.4.3 Zero Touch Provisioning (ZTP)
2.4.4 Bootstrapping
2.5 Configure authorization, authentication, and device access
2.5.1 Role-based access control for authorization
2.5.2 Different methods used to authenticate
2.5.3 The authentication sequence
2.5.4 The device access method
2.6 Configure and manage certificates
2.6.1 Usage
2.6.2 Profiles
2.6.3 Chains
2.7 Configure routing
2.7.1 Dynamic routing
2.7.2 Redistribution profiles
2.7.3 Static routes
2.7.4 Path monitoring
2.7.5 Policy-based forwarding
2.7.6 Virtual router versus logical router
2.8 Configure NAT
2.8.1 NAT policy rules
2.8.2 Security rules
2.8.3 Source NAT
2.8.4 No NAT
2.8.5 Use session browser to find NAT rule name
2.8.6 U-Turn NAT
2.8.7 Check HIT counts
2.9 Configure site-to-site tunnels
2.9.1 IPSec components
2.9.2 Static peers and dynamic peers for IPSec
2.9.3 IPSec tunnel monitor profiles
2.9.4 IPSec tunnel testing
2.9.5 Generic Routing Encapsulation (GRE)
2.9.6 One-to-one and one-to-many tunnels
2.9.7 Determine when to use proxy IDs
2.10 Configure service routes
2.10.1 Default
2.10.2 Custom
2.10.3 Destination
2.10.4 Custom routes for different vsys versus destination routes
2.10.5 How to verify service routes
2.11 Configure application-based QoS
2.11.1 Enablement requirements
2.11.2 QoS policy rule
2.11.3 Add DSCP/TOS component
2.11.4 QoS profile
2.11.5 Determine how to control bandwidth use on a per-application basis
2.11.6 Use QoS to monitor bandwidth utilization
3.1 Configure App-ID
3.1.1 Create security rules with App-ID
3.1.2 Convert port and protocol rules to App-ID rules
3.1.3 Identify the impact of application override to the overall functionality of the
firewall
3.1.4 Create custom apps and threats
3.1.5 Review App-ID dependencies
3.2 Configure GlobalProtect
3.2.1 GlobalProtect licensing
3.2.2 Configure gateway and portal
3.2.3 GlobalProtect agent
3.2.4 Differentiate between login methods
3.2.5 Configure Clientless VPN
3.2.6 Host information profile (HIP)
3.2.7 Configure multiple gateway agent profiles
3.2.8 Split tunneling
3.3 Configure decryption
3.3.1 Inbound decryption
3.3.2 SSL forward proxy
3.3.3 SSL decryption exclusions
3.3.4 SSH proxy
3.4 Configure User-ID
3.4.1 User-ID agent and agentless
3.4.2 User-ID group mapping
3.4.3 Shared User-ID mapping across virtual systems
3.4.4 Data redistribution
3.4.5 User-ID methods
3.4.6 Benefits of using dynamic user groups in policy rules
3.4.7 Requirements to support dynamic user groups
3.4.8 How GlobalProtect internal and external gateways can be used
3.5 Configure WildFire
3.5.1 Submission profile
3.5.2 Action profile
3.5.3 Submissions and verdicts
3.5.4 Signature actions
3.5.5 File types and file sizes
3.5.6 Update schedule
3.5.7 Forwarding of decrypted traffic
3.6 Configure Web Proxy
3.6.1 Transparent proxy
3.6.2 Explicit proxy
4.1 Configure templates and template stacks
4.1.1 Components configured in a template
4.1.2 How the order of templates in a stack affects the configuration push to a
firewall
4.1.3 Overriding a template value in a stack
4.1.4 Configure variables in templates
4.1.5 Relationship between Panorama and devices as pertaining to dynamic
updates versions, policy implementation, and/or HA peers
4.2 Configure device groups
4.2.1 Device group hierarchies
4.2.2 Identify what device groups contain
4.2.3 Differentiate between different use cases for pre-rules, local rules, the
default rules, and post-rules
4.2.4 Identify the impact of configuring a primary device
4.2.5 Assign firewalls to device groups
4.3 Manage firewall configurations within Panorama
4.3.1 Licensing
4.3.2 Commit recovery feature
4.3.3 Automatic commit recovery
4.3.4 Commit types and schedules
4.3.5 Config backups
4.3.6 Commit type options
4.3.7 Manage dynamic updates for Panorama and Panorama-managed devices
4.3.8 Software and dynamic updates
4.3.9 Import firewall configuration into Panorama
4.3.10 Configure log collectors
4.3.11 Check firewall health and status from Panorama
4.3.12 Configure role-based access on Panorama
5.1 Manage and configure Log Forwarding
5.1.1 Identify log types and criticalities
5.1.2 Manage external services
5.1.3 Create and manage tags
5.1.4 Identify system and traffic issues using the web interface and CLI tools
5.1.5 Configure Log Forwarding profile and device log settings
5.1.6 Log monitoring
5.1.7 Customize logging and reporting settings
5.2 Plan and execute the process to upgrade a Palo Alto Networks system
5.2.1 Single firewall
5.2.2 HA pairs
5.2.3 Panorama push
5.2.4 Dynamic updates
Task 5.3 Manage HA functions
5.3.1 Link monitoring
5.3.2 Path monitoring
5.3.3 HA links
5.3.4 Failover5.3.5 Active/active and active/passive
5.3.6 HA interfaces
5.3.7 Clustering
5.3.8 Election setting
6.1 Troubleshoot site-to-site tunnels
6.1.1 IPSec
6.1.2 GRE
6.1.3 One-to-one and one-to-many tunnels
6.1.4 Route-based versus policy-based remote hosts
6.1.5 Tunnel monitoring
6.2 Troubleshoot interfaces
6.2.1 Transceivers
6.2.2 Settings
6.2.3 Aggregate interfaces, LACP
6.2.4 Counters
6.2.5 Tagging
6.3 Troubleshoot decryption
6.3.1 Inbound decryption
6.3.2 SSL forward proxy
6.3.3 SSH proxy
6.3.4 Identify what cannot be decrypted and configure exclusions and bypasses
6.3.5 Certificates
6.4 Troubleshoot routing
6.4.1 Dynamic routing
6.4.2 Redistribution profiles
6.4.3 Static routes
6.4.4 Route monitoring
6.4.5 Policy-based forwarding
6.4.6 Multicast routing
6.4.7 Service routes
6.5 General Troubleshooting
6.5.1 Logs
6.5.2 Packet capture (pcap)
6.5.3 Reports
6.6 Troubleshoot resource protections
6.6.1 Zone protection profiles6.
6.2 DoS protections
6.6.3 Packet buffer protections
6.7 Troubleshoot GlobalProtect
6.7.1 Portal and Gateway
6.7.2 Access to resources
6.7.3 GlobalProtect client
6.8 Troubleshoot policies
6.8.1 NAT
6.8.2 Security
6.8.3 Decryption
6.8.4 Authentication
6.9 Troubleshoot HA functions
6.9.1 Monitor
6.9.2 Failover triggers
- Use Firewall tools, including the WebUl and CLI, to investigate networking issues.
- Follow proven troubleshooting methodologies that are specific to individual features.
- Understand the Flow-Logic used by the Next-Generation Firewall
- Learn how to configure and enable Packet Capture and advanced Packet-Level Diagnostic Features
- Identify necessary System Daemons and their logs to resolve various real-life scenarios.
- Solve numerous advanced, scenario-based challenges.
- Troubleshoot common issues related to firewall deployment.
- Troubleshoot connectivity problems.
- Troubleshoot policy and NAT-related Issues.
- Troubleshoot User-D
- Troubleshoot Site-to-Site VPN problems.
- Troubleshoot Global Protect™ related issues.
- Identify performance problems.
- How to use the Customer Support Portal
lab infrastructure.

Palo Alto Networks Cerified Network Security Engineer equipment and software list:


Palo Alto Networks technology is highly integrated and automated. The Palo Alto Networks product portfolio comprises multiple separate technologies working in unison to prevent successful cyberattacks. The Palo Alto Networks Certified Network Security Engineer (PCNSE) demonstrates that engineers can correctly deploy and configure Palo Alto Networks Next-Generation Firewalls while leveraging the rest of the platform
Physical Equipment
- Palo Alto Networks PA-220
- Palo Alto Networks PA-440

Virtual Machines
- Palo Alto Networks VM-50
- Palo Alto Networks PAN-OS 11.0
- Palo Alto Networks Panorama Virtual Appliances 11.0
Supporting Machines
- Test PC: Windows 10 Enterprise
- AD/DNS: Window Server 2016
- Linux Kali
Topology
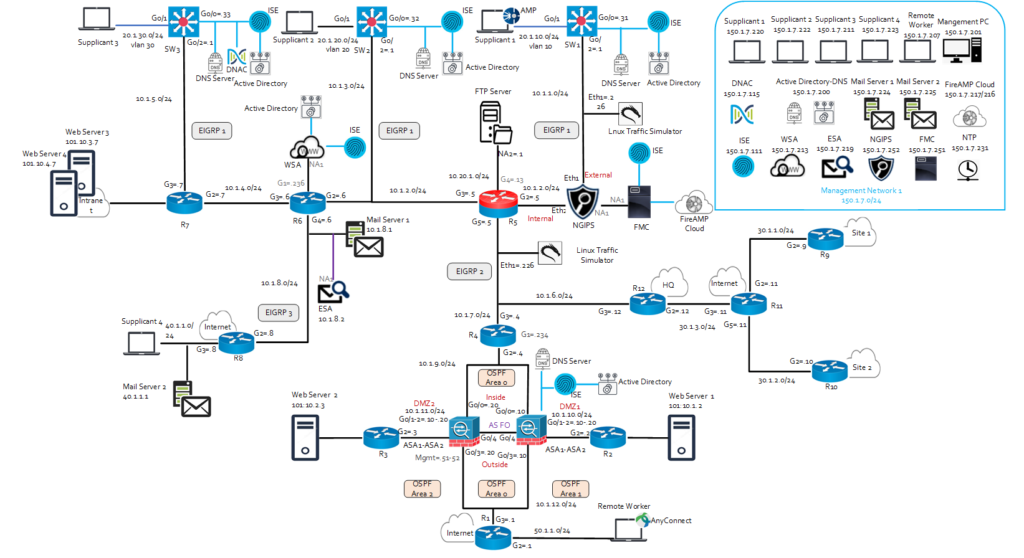

Modes Of Training
We provide various modes of training, each catering to different learning styles, preferences, and needs.You can make your choice of training mode.
- Classroom-Based Training
- One-On-One Training
- Online Training
- Corporate Training
- Fast Track Training
- Private Group Training
- Lab Workshop Training
Instructors

MD & Founder
4XCCIE (R&S, Security, Collaboration, DC), PCNSE & NSE7
Gigi Vikraman a quadruple CCIE has over 15 years of experience working in the Cisco networking field consulting and training. In addition, he has designed, implemented and supported numerous enterprise networks. He has been a dedicated CCIE instructor for over 10 years. He has extended his service in producing 400+ CCIE’s all over the world. Apart from all these, he has already proven his well knowledge in giving training on Fortinet, Palo Alto and Check Point.




